Scientists Filmed Plant ‘Talking’ to Its Neighbor, and the Footage Is Incredible
Invisible to us, flowers are surrounded by a ravishing mist of airborne compounds that they exercise to be in contact and offer protection to themselves. Luxuriate in scent, these compounds chase away hungry herbivores and warn neighboring flowers of incoming invaders.
Scientists include known about the protection of these flowers since the 1980s, since then they’ve been detected in better than 80 plant species. Now, a crew of Japanese researchers has deployed actual-time imaging ways to repeat how flowers receive and respond to those airborne alarms.
This grow to be as soon as a well-known gap in our working out of plant interactions: we knew how flowers ship messages, but no longer how they receive them.
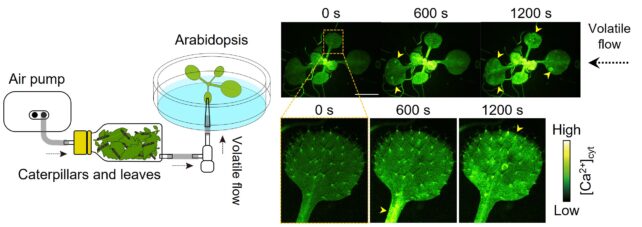
On this gaze, molecular biologists Yuri Aratani and Takuya Uemura of Saitama College in Japan and their colleagues noticed, with the back of a pump and a fluorescence microscope, the transfer of compounds emitted by injured and trojan horse-infested flowers to their undamaged neighbors. What came about.
frameborder=”0″ permission=”accelerometer; auto play; Clipboard-Write; encrypted-media; Gyroscope; portray in Checklist; internet-share” allowscreen>
Caterpillar (Spodoptera litura) include been grafted onto leaves harvested from tomato flowers and Arabidopsis thalianaA total weed within the mustard family, and researchers imaged the responses of a 2nd, intact, pest-free arabidopsis Plant trees at those risk indicators.
These flowers include been no regular weeds: They include been genetically altered so their cells contained a biosensor that glowed inexperienced when it detected an influx of calcium ions. Calcium signaling is one thing that human cells also exercise to be in contact.
The crew veteran a equivalent methodology to measure calcium signals in a gaze of fluorescence closing year mimosa pudica Vegetation that pass their leaves hasty in accordance with touch to address up away from predators.
This time, the crew visualized how flowers answered when bathed in unstable compounds that flowers start within seconds of being injured.
Experimental dwelling-as much as visualize calcium signaling arabidopsis Leaves. (Aratani et al. nature communication2023)
This grow to be as soon as no longer a pure affiliation; The compounds include been concentrated in a plastic bottle and pumped at a constant payment onto the recipient plant, but this allowed the researchers to review which compounds include been within the pungent combination.
As it’s seemingly you’ll presumably maybe watch within the video above, the broken flowers purchased messages from their injured neighbors loud and obvious, responding with a burst of calcium signals that rippled one day of their outstretched leaves.
Inspecting airborne compounds, the researchers stumbled on that two compounds, called Z-3-HAL and E-2-HAL, precipitated calcium signals. arabidopsis,
They also identified which cells respond first to risk signals by engineering arabidopsis Vegetation with fluorescent sensors specifically in guard, mesophyll or epidermal cells.
Guard cells are bean-formed cells on the surfaces of flowers that carry out stomata, minute pores that start to the ambiance when flowers 'breathe' in CO2. Mesophyll cells are the interior tissue of leaves, and epidermal cells are the outermost layer or pores and skin of plant leaves.
When? arabidopsis In flowers uncovered to Z-3-HAL, guard cells generated calcium signals within a minute or two, after which mesophyll cells picked up the message.
Furthermore, pre-medication of flowers with phytohormones that shut stomata greatly reduces calcium signaling, suggesting that stomata characteristic because the 'nostrils' of the plant.
“We now include at closing unraveled the advanced story of when, where and how flowers respond to airborne 'warning messages' from their unhealthy neighbors,” says Masatsugu Toyota, a molecular biologist at Saitama College in Japan and senior writer of the gaze.
“This ethereal communication network, hidden from our look for, performs a a will need to include characteristic in conserving neighboring flowers safe in time from drawing shut threats.”
The gaze has been printed in Nature communication.
Supply
Source credit : crast.net